Metadata

What is Metadata?
Metadata provides information about data.
Why is Metadata Important?
It provides information that helps consumers find, use, and understand the data’s quality and where it came from. Metadata also demonstrates how data is related to provide context for users.
Types of Metadata
It can be classified into the following categories:
- Descriptive Metadata includes information such as the author, creation date, modification date, and size.
- Structural Metadata describes how compound data is structured. For example, a single string might contain multiple fields, including variable field length information and datatype.
- Administrative Metadata provides management information, such as how often it needs to be refreshed to remain useful.
- Reference Metadata records information about the quality of the data and source.
- Legal Metadata records the copyright holder, usage limitations, and licensing requirements.
How it’s Used
Metadata fulfills multiple functions. Cataloging the data is important as it informs users of its quality, completeness, provenance, and authoritativeness. Images can have associated metadata, including digital signatures, creation dates, geographic locations, size and color depth. Exchangeable Image File (EXIF) data is a standards-based metadata embedded within the image file.
The Data Lakehouse provides metadata that significantly enhances the value of the data sets it maintains by documenting the data quality and relationships between different data assets.
Database management systems maintain it in system catalogs that record the number of records in a table, the cardinality of the data fields, high-water marks and low-water marks, the selectivity of indexes, and the clustering of data to indexes.
Modern web-based applications use application programming interfaces (APIs) to access third-party tools and pass data using metadata-rich datatypes such as JSON and XML. Traditional applications passed data between them, but it was not self-describing, and you could not interrogate them to learn what data they were expecting as you can with a modern web service. As applications become more componentized to be more easily used to build new apps, their numbers will grow, increasing their need to self-document their function and data needs.
Benefits of Metadata
The need for metadata is growing primarily due to the following benefits:
- It increases the usefulness of existing data sources.
- It makes data useful by documenting its quality and utility.
- It includes labels that enable data to be found using search engines.
- It promotes data governance by documenting data owners or their absence.
- As data volumes and sources grow, it becomes increasingly valuable.
- The use of data is a best practice of data management that benefits the data owner and business partners that share data. Data sharing success is dependent on good metadata. Data that is not well documented is likely to be unused or trusted.
- It is a foundational pillar of advanced data models such as data warehouses, data lakes, and data mesh.
- It supports the records discovery process for compliance audits.
- The visibility gained by using it to document an organization’s data assets is the first step in streamlining data use so duplicate data can be reviewed, merged or removed.
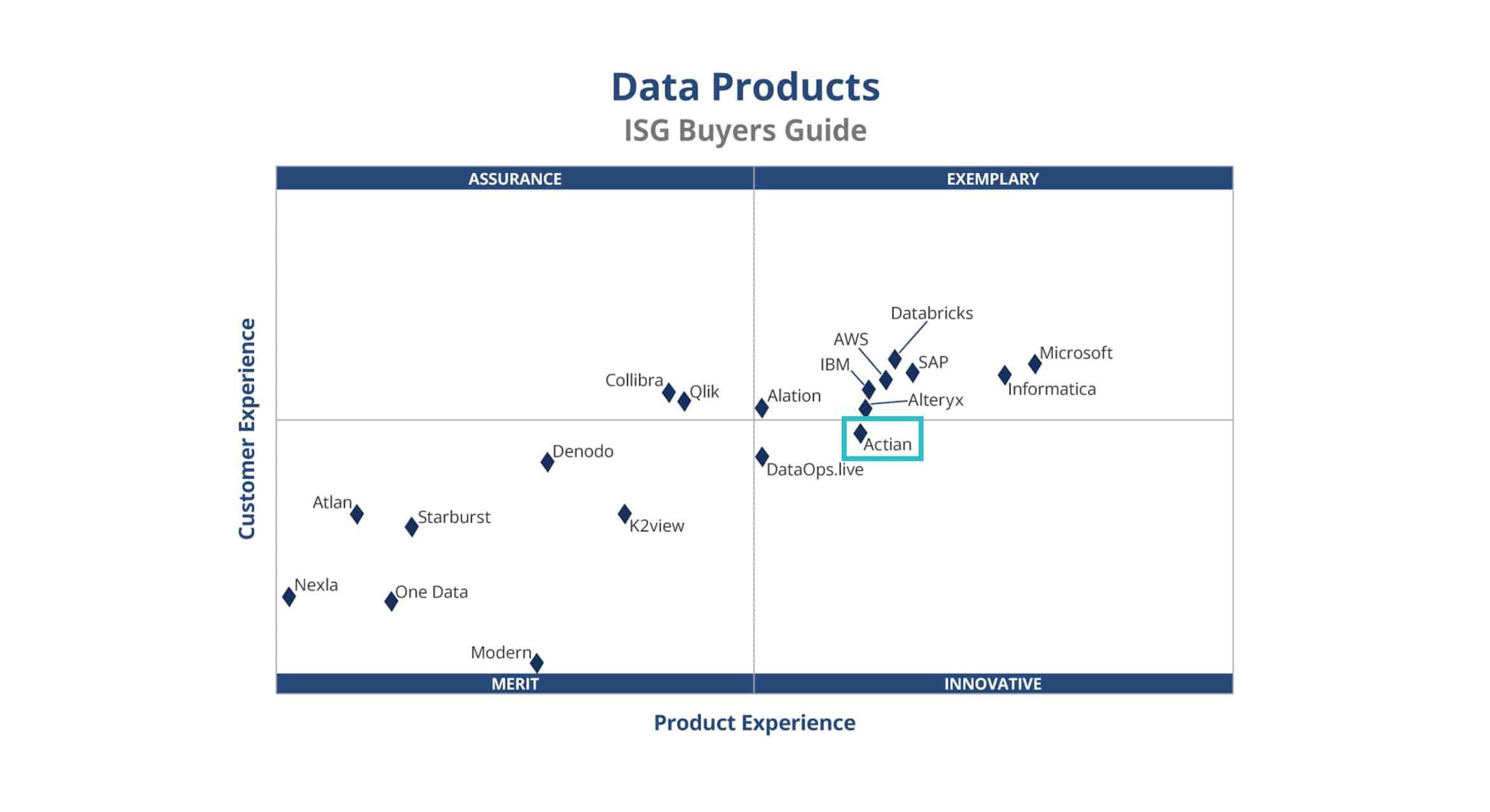
Actian
The Actian Data Platform makes it easy to create high-performance data warehouses. The integrated columnar, vectorized database uses a superior parallel query capability for faster query results. External data can be registered to the data warehouse to be accessed as easily as an internal object. Data connectors include Hadoop Spark. Multiple distributed database instances can be accessed using a single SQL query to support federated data models.
Offering built-in data integration-as-a-service connects to hundreds of data sources and can be used to document, extract, and load both file-based and streamed data. Actian lets you connect to REST and SOAP APIs to create and manage integrations.
The Actian Data Platform works with popular data storage structures that include S3 buckets, Google Drive folders and Azure Blob storage. Instances can be deployed to multiple cloud platforms using a standard user interface and management console.