How Does a Data Fabric Differ from a Data Mesh?
A data fabric is a single virtual centralized system with centralized data ownership and stewardship. A data mesh uses a federated set of domain-specific data product services with stewardship and data ownership at the domain level. The data mesh is more of a peer-to-peer model with domains sharing data horizontally.
Why Use Data Fabric?
A data fabric is designed to make high-quality, secure data and insights available to any user, anywhere. It is a holistic approach for accessing all the available data assets in a business regardless of location.
This replaces traditional point-to-point data integrations with a consistent integration layer. Machine learning models, for example, need access to large amounts of data to train them, as more extensive data sets result in more accuracy. Metadata in the data fabric is connected by knowledge graphs which help connect related data sources.
The whole business can enjoy ubiquitous data access regardless of what hardware or cloud it runs on. Both structured and unstructured data are accessible with a consistent user experience.
An approach of this nature to data infrastructure is the answer to the escalating costs of maintaining a heterogeneous environment by bringing all storage and access services under one unified umbrella.
Getting Started With a Data Fabric Project
The first step in initiating a data fabric is to build a cross-functional team of data owners, consumers, and infrastructure professionals. Existing systems and integrations need to be cataloged. The most business-critical insights will need to be prioritized.
The user experience needs to be architected, designed, built, tested, and refined.
A cross-platform data management system needs to be selected. Ideally, one that can reside on-premise and in multiple clouds. The Actian Data platform is such a solution.
Storage needs to be easily accessible and elastic. This would be a good time to adopt block storage in the cloud which is more efficient and can be assigned elastic compute resources as user load increases without sacrificing performance.
Data replication technology maintains geographically local copies of critical data if network latency becomes a significant bottleneck.
The Benefits of a Data Fabric
The primary benefits of it include the following:
- More data-driven decision-making and easy access to high-quality, trusted data.
- Higher business agility to ready access to AI/ML insights.
- A consistent user experience around the globe regardless of data format.
- Secure access to data protected by firewalls, encryption, and strong authentication protocols.
- Lower training and infrastructure costs due to more standardized integrations and services.
- Futureproofed architecture for new projects to build upon.
- More metadata, cataloging.
- Better regulated data to support compliance and governance efforts.
- Fewer point-to-point data integrations to support thanks to the integration bus approach that a data fabric provides.
- Data becomes more of a utility as both professional data scientists, and casual data analysts can easily access necessary data and insights.
- Knowledge graphs map relationships between data elements to make data discovery and exploration easier for technical and non-technical users.
- The user-facing data consumption layer hides the complexity of accessing underlying data using APIs and SDKs from data consumers.
- End-to-end security is achieved thanks to the transport layer applying source-to-user encryption.
Potential Pitfalls
- Pick smaller systems to test your model or risk failure at an early stage.
- Include citizen analysts as data fabric testers to make it as usable as possible.
- Build in feedback mechanisms to keep the mesh updated with needed features or risk creating another stagnating data lake.
- Instrument existing systems to ensure you don’t waste energy migrating unused systems to the data fabric.
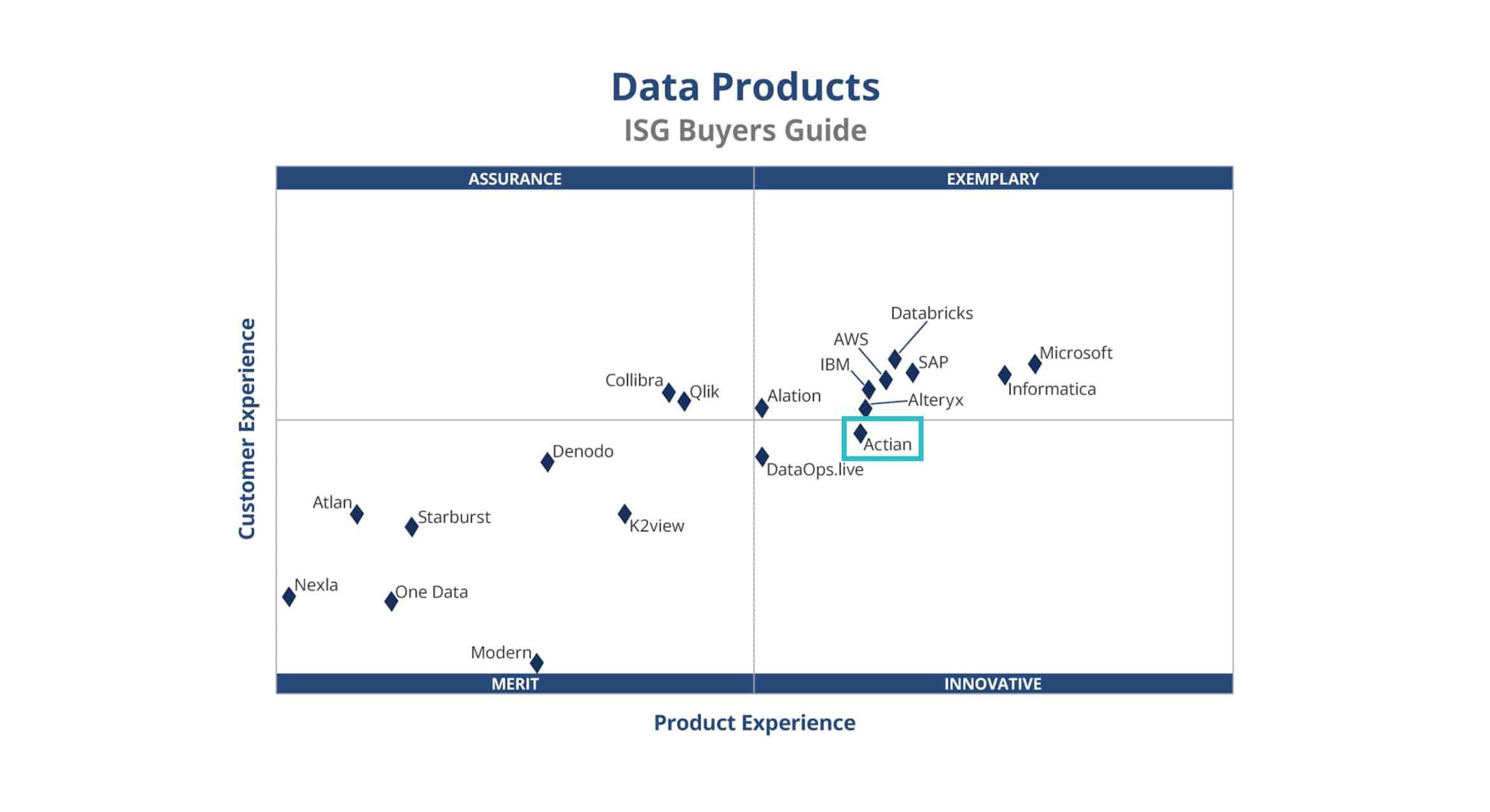
The Actian Data Platform
The Actian Data Platform can underpin a data fabric implementation by supporting data stored and analyzed on-premise or multiple cloud platforms. Actian eases integration with its built-in connectors to hundreds of prebuilt connectors to sources, including NetSuite, Salesforce and ServiceNow. The Actian Data Platform uses a vectorized columnar database that outperforms alternatives by 7.9x to deliver answers faster.
Data Fabric
A data fabric provides a centrally managed data and data integration service that offers a hybrid, multi-cloud data environment and a consistent user experience. A single one can serve a global user base with real-time unified data.
Data Locations
Data in a fabric can reside on-premise or in private or public cloud platforms.
Data
The data in a fabric can be in the form of metadata, in warehouses, documents, databases or applications.
Services
It provides services that include data storage, pipelines, provisioning, transport, orchestration, data ingestion, cataloging, and governance.