Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities
Actian Corporation
March 17, 2025

Today, organizations must ensure that their data is properly managed, secured, and utilized to drive business success. Effective data governance is crucial for regulatory compliance, data quality, and informed decision-making.
A well-defined governance structure improves operational efficiency and protects data assets from potential risks. To implement a strong data governance strategy, organizations must establish clear roles and responsibilities. This article explores the key roles in data governance, effective data governance team structure, and best practices for implementation.
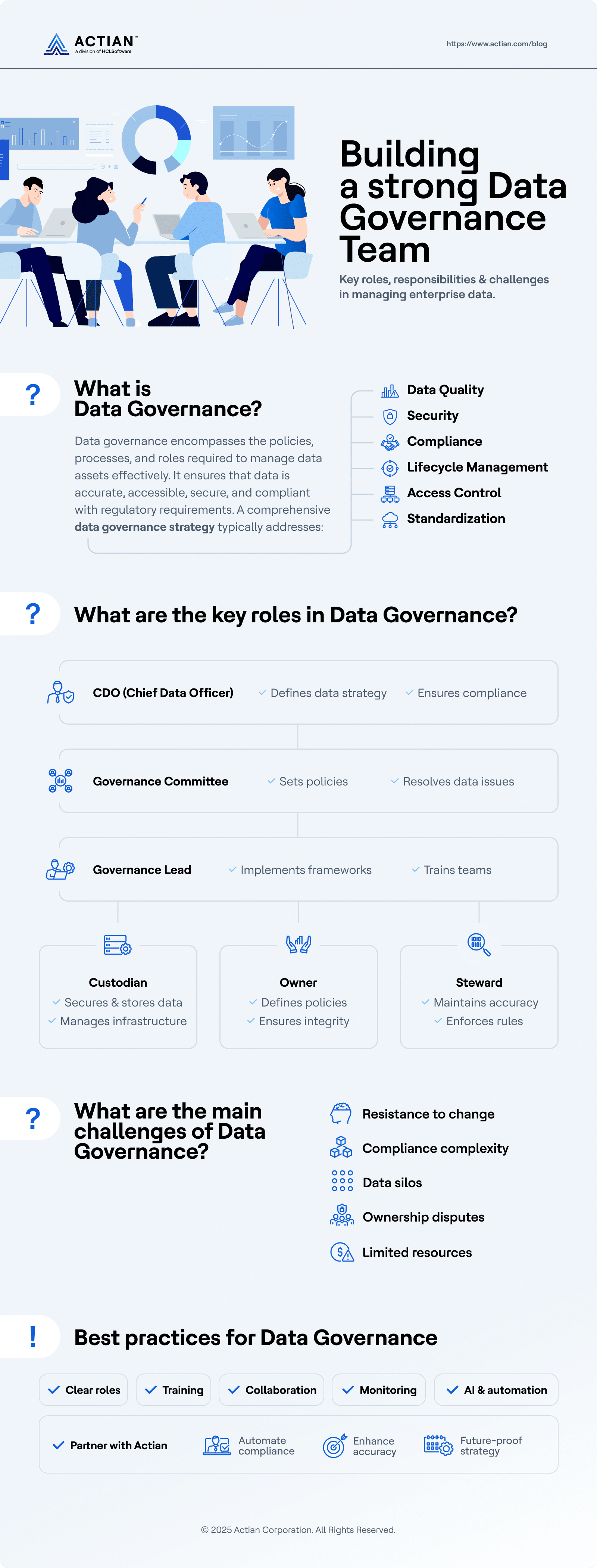
What Does Data Governance Cover?
Data governance encompasses the policies, processes, and roles required to manage data assets effectively. It ensures that data is accurate, accessible, secure, and compliant with regulatory requirements. A comprehensive data governance strategy typically addresses data quality, security, compliance, lifecycle management, access control, and standardization. Organizations must develop clear policies and frameworks that align with their business objectives and regulatory requirements to manage data efficiently. Understanding the role of data quality in data governance is a crucial aspect of this process.
An effective governance model also ensures data consistency across different systems, allowing organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions. By implementing governance protocols, businesses can reduce redundancies, streamline workflows, and maintain data integrity. Additionally, regulatory laws such as GDPR and HIPAA require organizations to establish robust data management protocols, making governance a critical compliance necessity.
Key Roles in Data Governance
When establishing your organization’s data governance framework, you will likely develop your own list of important roles. Below, we’ve listed a few common types of roles, a brief description of who that role represents, and a bulleted list of their responsibilities.
Chief Data Officer (CDO)
The Chief Data Officer is often the leader of a company’s data governance structure. As part of the senior executive suite, the CDO ultimately governs how the organization handles, stores, and uses its data.
- Responsible for defining and executing the organization’s data strategy.
- Oversee data governance policies and frameworks.
- Ensure compliance with data regulations and security standards.
- Promote data-driven decision-making across the organization.
- Lead data governance initiatives and align them with business objectives.
Data Governance Committee
Alternatively, in some organizations, data governance is not handled by a CDO. Instead, a group of executives and team leaders come together to form a committee that establishes a data governance methodology.
- Composed of cross-functional leaders from IT, compliance, and business units.
- Set up and enforce data governance policies and priorities.
- Approve data standards and resolve data-related disputes.
- Ensure alignment between data governance initiatives and business strategy.
- Provide oversight for data-related risks and compliance challenges.
Data Governance Lead
Hierarchically below the CDO or Data Governance Committee, the data governance lead is the professional in charge of spearheading the strategic implementation of an organization’s overall governance framework.
- Manage the implementation of data governance policies and frameworks.
- Coordinate efforts across various data stakeholders.
- Monitor compliance with established data policies and best practices.
- Provide training and awareness programs on data governance.
- Act as a liaison between executive leadership and operational teams.
Data Custodian
Data custodians are the individuals who develop technical methods by which an organization’s data is stored and processed. They help ensure the safety of organizational data.
- Handles the technical aspects of data governance, typically within IT departments.
- Implements data security measures and access controls.
- Ensure proper storage, backup, and archival of data.
- Manage data infrastructure and technology solutions.
- Support data lifecycle management processes.
Data Owner
Anyone within an organization who manages a specific set of data assets is considered a data owner. They oversee their data assets and typically make strategic decisions regarding the data asset
- Hold accountability for specific datasets within an organization.
- Define data usage policies and access permissions.
- Ensure data quality and integrity within their domain.
- Approve modifications to data structures and definitions.
- Collaborate with Data Stewards and Custodians to enforce governance policies.
Data Steward
The data steward is sometimes confused with the data custodian. While the custodian is the person who handles the technical aspects of data security and storage, the data steward is the one who uses the tools to ensure that the organization complies with its overall data governance strategy.
- Work within business units to ensure data quality and governance compliance.
- Monitor data integrity and resolves inconsistencies.
- Enforce data governance policies at an operational level.
- Provide support for data-related inquiries and issues.
- Collaborate with IT teams to implement data standards and controls.
Building an Effective Data Governance Team
Creating a successful data governance team requires careful planning and collaboration. Organizations should define roles and responsibilities clearly, ensuring that all team members understand their specific duties. Cross-departmental collaboration is essential, involving stakeholders from IT, compliance, and business units to ensure alignment. Investing in training and education programs helps equip team members with the necessary skills and knowledge. Establishing clear communication channels within the organization ensures that data governance policies and procedures are effectively implemented and understood by all relevant parties. Following data governance best practices is crucial in this effort.
Additionally, organizations must establish a governance framework that includes continuous monitoring, reporting, and auditing mechanisms. Setting key performance indicators (KPIs) can help organizations measure the success of their governance strategy and make necessary improvements over time.
Implementing a Data Governance Framework
A strong data governance framework provides a structured approach to managing data. Organizations should start by assessing their current data governance maturity and identifying gaps. Defining clear data governance goals aligned with business priorities ensures strategic direction. Developing detailed policies and procedures for data quality, security, and compliance establishes consistency. Assigning roles and responsibilities across teams ensures accountability and effective execution. Implementing data governance technology solutions helps streamline policy enforcement, while continuous monitoring and measurement ensure ongoing improvements in governance effectiveness. Some organizations may have data generated from IoT or edge devices, so it is essential to consider the importance of data governance for the Internet of Things (IoT).
A robust governance framework should incorporate automation tools to enhance efficiency. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies can help identify data anomalies, detect compliance violations, and improve overall data accuracy. Companies should also consider leveraging cloud-based governance solutions to manage large-scale data operations effectively.
Challenges in Data Governance
Despite its importance, data governance presents several challenges for organizations. Resistance to change can hinder adoption, as employees may be reluctant to modify existing processes. Data silos across different departments can create inconsistencies and inefficiencies. Navigating complex and evolving regulatory requirements requires constant attention and adaptation. Limited resources can make it difficult to allocate dedicated personnel and technology investments for governance initiatives.
Disputes over data ownership and access control can create conflicts between departments. Addressing these challenges requires strong leadership, a culture of data accountability, and the adoption of automation tools to streamline governance processes. A solid foundation in enterprise data governance can help organizations mitigate these challenges effectively.
To overcome these challenges, organizations must foster a data-driven culture where governance is integrated into daily operations. Conducting regular training programs, adopting scalable governance technologies, and establishing executive sponsorship ensures long-term success.
Partner With Actian for Your Data Governance Needs
Actian offers practical data management solutions designed to help organizations implement effective data governance strategies. With a comprehensive suite of tools for data integration, security, and analytics, Actian enables businesses to improve data quality, enhance regulatory compliance, and optimize governance processes.
By leveraging automation and AI-driven insights, Actian helps organizations streamline data governance while reducing data risks. Partnering with Actian ensures a strong foundation for data governance and allows organizations to maximize the value of their data assets. Learn how to build a future-proof strategy to optimize your data governance approach.
To further enhance your data governance framework, explore the Actian Zeenea Data Intelligence Platform to enable effective discovery, governance, and utilization of enterprise data assets.
Subscribe to the Actian Blog
Subscribe to Actian’s blog to get data insights delivered right to you.
- Stay in the know – Get the latest in data analytics pushed directly to your inbox.
- Never miss a post – You’ll receive automatic email updates to let you know when new posts are live.
- It’s all up to you – Change your delivery preferences to suit your needs.